- 13,372 ৳ Imran L.
- 13,403 ৳ Mizan S.
- 19,516 ৳ Nazim U.
- 15,449 ৳ Niyaz V.
- 11,872 ৳ Rishan B.
- 7,763 ৳ Yahya U.
- 17,550 ৳ Abrar Y.
- 7,181 ৳ Anik E.
- 12,019 ৳ Fahad Q.
- 6,128 ৳ Farid U.
- 4,373 ৳ Mashrur N.
- 17,710 ৳ Miraz P.
- 5,501 ৳ Nasif U.
- 2,621 ৳ Ripon F.
- 2,653 ৳ Rizwan G.
- 4,162 ৳ Sarfaraz R.
- 5,349 ৳ Shahed S.
- 2,107 ৳ Tauhid F.
- 10,549 ৳ Yakub K.
Babu88 Live & Online Casino Site in Bangladesh

100% Welcome Bonus
After registration you can choose one of 4 welcome rewards

Sports Bonuses in Babu88
Receive a reward for your first Babu88 deposit on sports

The Babu88 site is one of the best places for gamblers from Bangladesh. The casino is aimed specifically at the Bangladeshi audience and offers hundreds of casino games and dozens of sports, including cricket. Payments are made easily thanks to local payment systems, and it is possible to multiply your bankroll with generous bonuses.
Create an account in Babu88 Bangladesh and increase your initial deposit up to 100%. The biggest sum is ৳18,000. It is also possible to activate the BBRGWIN2 promo code to get extra funds.
About the Babu88 Casino Bangladesh
Babu88 website was launched in 2021 and over the years it has gained popularity and recognition among Bangladeshi users. Thanks to the Curaçao license, you can be sure of honesty and legality. The main advantage of the Babu88 site is the focus on the Bangladeshi audience, so it supports Bengali and the Bangladeshi taka as a currency. Moreover, the brand is the official sponsor of Montreal Tigers, Colombo Strikers, and Northern Warriors.

| About Casino |
Year of Foundation: 2021 Allowed Bangladeshi takas: Yes |
| Services |
|
| Deposit and Withdrawal Methods |
Deposit Withdrawal Currencies: Bangladeshi takas Min. Deposit: ৳200 Min. Withdrawal: ৳800 |
| Welcoming Bonus |
|
| Mobile App |
|
| License |
 Curacao license #365/JAZ |
| Customer Support |
|
Popular slots
-

Super Ace
-

Party Night
-

Boxing King
-

King Pharaoh
-

RomaX
-

Golden Chicken
-

Money Coming
-

Crazy Hunter
Babu88 Live casino
If you want to go to a casino and play for real, but you don’t have time for that, then this site has something to offer you. Babu88 Live casino is the place where you can play your favorite table games such as blackjack, roulette, and baccarat with real dealers right from your home. They are collected under the Live Casino tab.

| Providers | Pragmatic Play, Evolution Gaming, AE Casino, Playtech, Royal Gaming, Ezugi, Aura |
| Number of Games | 600+ |
| Game Genres | Blackjack, Baccarat, Roulette, Sic Bo, TV Shows, Monopoly, Dragon Tiger, Dice, Poker, Teen Patti |
| Best Games | Hindi Baccarat, Evo Speed Blackjack, Super Sic Bo, Mega Ball, Crazy Time |
Advantages of the Babu88 Casino
Casino Babu88 has many advantages for which it is loved by players from Bangladesh. You should pay attention to:
- Focus on Bangladesh – The Babu88 website and app have done everything for the convenience of Bangladeshi players. The interface is in Bengali, and you can conduct transactions in BDT through familiar Bangladeshi payment systems like Nagad;
- Sportsbook – Saba Sports, which partners with Babu88, offers players 40 sports to bet on. Among this number, you can find both popular disciplines like cricket and kabaddi, as well as cybersports. The site pays special attention to cricket because it is extremely popular in Bangladesh;
- Security – You can rest assured about the security of your data, as Babu88 pays serious attention to this issue. Your data and transactions are under 256-bit SSL encryption, which keeps everything protected. The casino games offered by Babu88 have RNG and Provably Fair mechanisms that guarantee the fairness of every round;
- Casino Library – You will find 2,500 games from more than 20 renowned providers. This collection has everything that players love so much, including slot games, crash games, fishing games, and Babu88 Live casino;
- Support – If you have any questions or problems you can always rely on Babu88’s support team. The support agents are available round the clock, ready to help you at any minute. You can choose any of the available methods including live chat, email, and social media.

Babu88 Bonus Offers for Bangladeshi Players
An undeniable advantage of Babu88 is the number of promotions. Thanks to this, players from Bangladesh can increase the amounts of their deposits and get other prizes, in particular gifts for their birthdays, cashback, and reload rewards.
The most notable advantage is that Babu88 offers players 4 welcome bonuses to choose from, depending on what they prefer.

| Bonus type | Minimum top-up | Maximum bonus amount | Wagering requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sports | ৳800 | ৳12,000 | 13x |
| Slots | ৳800 | ৳18,000 | 18x |
| Crash | ৳800 | ৳10,000 | 20x |
| Live Casino | ৳800 | ৳13,000 | 18x |
VIP Program of Babu88
Special mention should be made of the VIP program from Babu88 BD. Under the terms of this promotion, you can invite friends and get a lifetime 2% commission when the referred user makes a deposit.
To get the bonus, the friend you invited must deposit at least ৳2,000 and spend at least ৳5,000 in total. If these conditions are met you will both receive ৳500 each. This amount is subject to a 3x wager.
Coming back to the commission, it should be clarified that you will receive it every time your invited friend makes a deposit. The amount of your commission will depend on the percentage ratio and will be credited to your referral wallet.

How to join Babu88
Any user can join the Babu88 BD and play games. For this purpose, they need to go through a couple of simple stages after which they will be able to use the site functionality to the fullest.

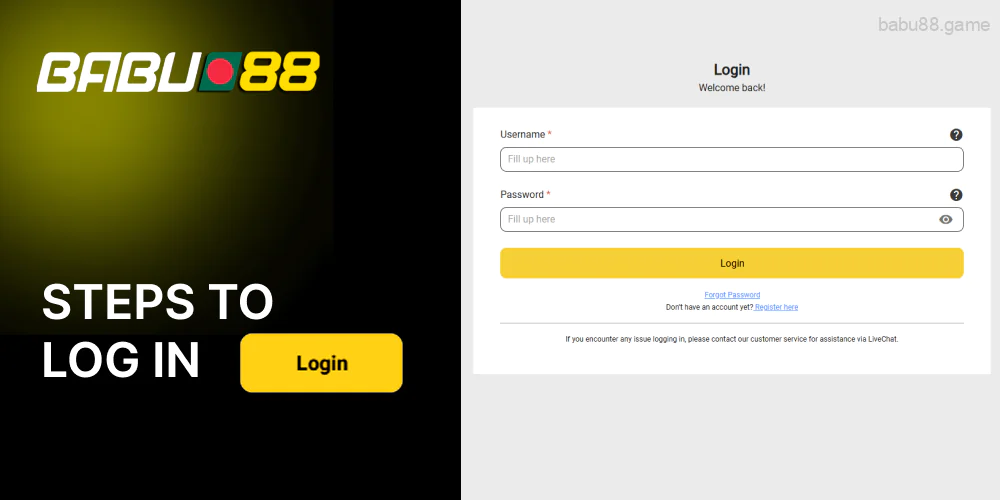
Steps to Log In to Babu88
After signing up, you are authorized automatically but can be logged out from time to time due to security reasons. In case you need to re-enter your account, it won’t cause any problems. Just follow these guidelines:
- Go to the Babu88 BD website.
- Look at the top right corner and click on the black “Login” button.
- In the form that appears, you need to enter the username and password that you specified during registration.
- Check the correctness of the entered data and click on the black “Login” area at the bottom to enter your account.
If you have forgotten your password, open the login form and under the password field click on the gray area “Forgot Password”. After that, you will only need to enter and verify the phone number specified during registration and change your password.
Verifying Your Identity
For you to be able to fully use your Babu88 account, in particular, to withdraw money, you will need to verify it. This is done in seconds, as described in the instructions:
- Log in and look at the top menu. There will be tools to manage your account on the right.
- Click on your nickname to open your profile settings. It is located to the left of the messages icon.
- Now find the “Primary Number” field, where you will need to click on the “Verify OTP” area highlighted in red.
- This will open the verification menu where you will need to enter the captcha and then click on the “Request OTP” button.
- Within 1-2 minutes you will receive an SMS with a confirmation code on your phone, which you will need to enter in the corresponding field, located to the right of the button you clicked.
- Check if the code is correct after entering it and click on the “Submit” area at the bottom.

How to play casino games in Babu88
If you are a beginner and have never used the Babu88 Live site before, you should familiarize yourself with the instructions on how to play
-
Step 1

Open the Babu88 website.
-
Step 2

Log in to your account.
-
Step 3

Make a deposit if necessary.
-
Step 4

Choose the category of games you are interested in in the top menu.
-
Step 5

Once you have made your selection, you will see a list of all the available games. Pick the one using filters or a search bar.
-
Step 6

When you have selected a game, click on it and wait for it to launch.
-
Step 7

Familiarize yourself with the rules and insert the bet size.
-
Step 8

Press “Play” or “Spin” and try to win.
Babu88 Online Casino for Bengali Players
The game collection on the Babu88 casino site is impressive with over 2,500 games. They are offered thanks to the cooperation with well-known developers like Pragmatic Play, Jili, or Spade Gaming. The collection is conveniently divided into several separate categories.

Slots
Babu88 slots is the most extensive category with over 1,500 games. The games are presented in a variety of themes and features and boast high RTP. In addition, the slots have different volatility – from low to high. The most popular games in the category are marked as Hot, and among them, you can find:
- Mayan Empire;
- Sugar Party;
- Super Ace;
- Money Coming;
- Fortune Gems.

Jackpot Games
Games in this category differ from regular slots in that they have a special jackpot that is replenished every time any player makes a bet in the game. These games are better known as progressive jackpot slots. Once won, the prize is credited to a winner, and the prize pool accumulation starts again. There are 12 jackpot games on the Babu88 casino site, and each one is worth a look. The most popular ones are the following:
- Pocket Mon Go;
- Railway King;
- Lucky Strike;
- Great Stars;
- Emperor Gate.

Megaways
This is a type of slot that utilizes Megaways mechanics, where the main difference from traditional slots is that the number of symbols on each reel changes with each spin, creating a huge number of possible ways to win. Megaways slots also often utilize cascading wins, where winning symbols disappear and new ones fall in their place, creating the opportunity for additional wins in a single spin. This is also a very popular variation of slots in the Babu88 casino, especially these games:
- Fire Blaze: Sky Queen;
- Rainbow Jackpots;
- Jungle Spirit;
- Primate King;
- Jelly Belly.

Table games
Babu88 casino table games need no introduction because even a user far from the world of casinos probably knows about poker, blackjack, and roulette. There are about 90 different versions on the site. These games are often played by experienced players, because of their complex, but intensely interesting rules. The most popular table games in Babu88 are:
- 7up7down;
- Sic Bo;
- 5CardPoker;
- Dragon & Tiger;
- Speed Baccarat.

Arcade games
Arcade casino games, also known as crash games or quick games, are fast-paced and differ from traditional slot machines or table games. There are 30+ of them on the site. Such games offer simple mechanics and rapid rounds that usually last only a few seconds and usually have intuitive rules that are easy for even beginners to learn. The most popular games in this Babu88 casino category are these:
- Go Rush;
- Aviator;
- NFT Aviatrix;
- CricketX;
- Balloon.

Fishing games
The games in this category have an interesting concept and yet are quite simple and fun. Your task is to place bets and catch fish. The bigger the bet, the bigger fish you can catch and therefore win more. You will find 11 games in this Babu88 category, among which are:
- Fishing God;
- Bombing Fishing;
- Jackpot Fishing;
- Mega Fishing;
- Happy Fishing.

Babu88 Live Games in Bangladesh
In addition to over 2,000 slots and other games, Casino Babu88 Live has more than 600 live games from 7 well-known providers. This format is ideal for those who love real casinos, but have no opportunity to go to it for one reason or another. Of course, live games will not be able to convey the whole atmosphere of the casino but will allow you to get as close to it as possible. The atmosphere is achieved by interacting with other real players and the croupier.

Live Baccarat
One of the most popular live table games on the site is baccarat, the task of which is to predict which hand – player or banker – will have a total value close to 9. You can find about 90 live variations of this famous Babu88 game. The most popular ones are:
- Sexy Baccarat;
- Hindi Baccarat;
- Gangnam Speed Baccarat;
- XXXtreme Lightning Baccarat;
- Jade Baccarat.

Live Roulette
For gamers from Bangladesh, there are about 130 live roulette games in the Babu88 live casino. Live roulette is played on a wheel with numbered pockets. The wheel has 37 or 38 numbered cells depending on the game variant. The object of the game is to predict where the ball will fall after the wheel spins. Here are some of the popular roulette games featured on the live Babu88 site:
- First Person Lightning Roulette;
- Cash Collect Roulette;
- Sticky Bandits Roulette;
- Cricket Auto Roulette;
- VIP Roulette.

Live Sic Bo
Sic Bo is a game originating from China that utilizes dice with numbers from 1 to 6. Bangladeshi players need to place bets on the various outcomes of the dice roll. The betting table contains various fields for placing bets on possible outcomes. The outcome of the roll is determined by the sum of the numbers on the three dice and the combinations, and the dealer announces the results and winnings. The Live Babu88 Casino offers you to play the following Sic Bo games with real croupiers:
- Super Sic Bo;
- Instant Super Sic Bo;
- Mega Sic Bo;
- Emperor Sic Bo;
- First Person Sic Bo.

Live Monopoly
Monopoly Live is a TV show-inspired game that combines elements of the classic board game Monopoly and Wheel of Fortune. Bengali players place bets on segments of the wheel and the host spins the wheel. There are two variations of this game in the Babu88 live casino, namely Monopoly Live and Monopoly Big Baller.

Live Crazy Time
Crazy Time in the Babu88 live BD casino offers players an interactive game show with four bonus games where prizes can increase significantly. The game is tied to a money wheel with additional features such as Top Slot. The wheel consists of 54 segments with numbers or bonus game icons.

Live Andar Bahar
Andar Bahar is a card game originally from India, which is available in a live casino format thanks to providers Evolution Gaming and Ezugi. The rules are very simple, which makes it popular with many Bangladeshi players. At the start of the game, the dealer draws one card from the deck, which becomes the main card, and players bet on one of the two sides. The following variations of this game are available on the Babu88 Live website:
- Ultimate Andar Bahar;
- OTT Andar Bahar Marina;
- Super Andar Bahar.

Live Blackjack
Babu88 offers Bangladeshi players about 100 live blackjack games. The main goal is to accumulate a sum of cards as close to 21 as possible, but not exceeding that number. Players compete against the dealer. Usually, several standard decks are used (4 to 8 decks of 52 cards). The following variations of blackjack are particularly popular in the Babu88 live casino:
- Jade Blackjack;
- Mega Fire Blaze Blackjack Live;
- Royal Blackjack 2;
- Unlimited Blackjack;
- Blackjack Platinum.

How to play Babu88 Live games in Bangladesh
You won’t need to do any complicated procedures to get started with Babu88 live games. If you want to figure it out, check out these instructions:
- Go to the Babu88 live website or mobile app.
- Log in to your account or create one if you don’t have it.
- Live games cannot be played in demo mode so you will need to fund your account. To do this, click on the gray-white plus icon at the top right of the screen and deposit BDT through any payment tool you like.
- Take a look at the top menu of the site, there you will see the game tabs. The second tab in this menu will be Babu88 Live Casino, click on it.
- You will see a general list of games. If you want to filter it out, you can choose a specific provider in the menu above or use the search box on the right.
- When you have decided on a game, click on it and wait for it to launch.
- Be sure to familiarize yourself with the rules of the game, place your bet, and wait for the dealer to start the next round.

Babu88 Sports Betting
The Babu88 live bet site provides access to betting on over 40 sports, including cybersports. There are over 2,000 matches available for live and pre-match betting on a daily basis. You can also bet on cricket there. The most popular sports are the following:
- Cricket;
- Kabaddi;
- Soccer;
- Basketball;
- Badminton;
- Table tennis.

Cricket betting
Cricket is the number one sport in Bangladesh. Every day you will have access to dozens of matches to bet on with 30-40 sports markets each, including Coin Toss Winner, Top Batsman, and Total Wickets. There are two cricket sportsbooks on the Babu88 bet site. You will be able to bet on the following tournaments:
- Bangladesh National Cricket League;
- Bangladesh Premier League;
- Indian Premier League;
- ICC World Cup T20;
- Pakistan Super League;
- Asia Cup;
- The Hundred.

Betting Pass
Bangladeshi bettors have access to a specific tab Betting Pass on the Babu88 bet website. With this promotion, you can earn cash rewards and real prizes by advancing the level. The more you bet, the bigger free bets and prizes are given. Among the real gifts you can win are:
- Yamaha R15M BS7;
- Samsung 75 QLED 4K Smart TV;
- iPhone 15 Pro Max 512 GB;
- iPad Pro 12.9 inch Wi-Fi (256 GB);
- Sony PlayStation 5;
- Gold Bar(5 Gram);
- AirPods Prod (2nd Generation).
Odds
You can find different odds formats on the Babu88 website. 5 of them are offered to Bangladeshi bettors:
- Decimal – It represents a bet’s potential profit, including the bet’s size. Decimal odds are more common as it is the easiest format to check chances. To calculate the potential win, simply multiply the amount you want to bet by the offered value (for example, 1.75);
- American – American odds are expressed as a positive or negative number. A negative number shows how much you have to bet to make a ৳100 profit, while a positive number shows how much profit you can make if you bet ৳100;
- Indonesian – The principle of operation is exactly the same as with the American format, but in this case, all odds are divided by 100;
- Malaysian – Malaysian odds are expressed in decimal format using plus (+) and minus (-) signs to indicate favorite and underdog. If the odds are 0, it means that the bet is 50/50 and will be paid out at even money;
- Chinese – These odds are very similar to the decimal bet type but differ. All odds differ by one, in the example 2.34 becomes 1.34, and 0.42 becomes 1.42. Thus, in the case of a bet of ৳100 at odds of 1.5, the player will receive ৳250.

System bets
You can make a system bet in Babu88 for a more strategic approach. With this bet type, the betslip contains 3 or more betting markets. You can create several combinations from them, a only part of the right guesses is enough for a payout (for example, 4 out of 6).
The amount of the bet is evenly distributed among all potential express bets that can be created in the system betslip.
E-sport betting
Bangladeshi bettors can try esports betting on the site. Babu88 features more than 10 of the most popular cybersports. Over 50 betting markets are offered for the top matches, and you can try to bet on these cybersports:
- League of Legends;
- Dota 2;
- Counter-Stike 2;
- Valorant;
- Kings of Glory.
Babu88 Mobile Apps for Bengali Players
Babu88 offers Bangladeshi users a modern Babu88 mobile application that is completely identical in functionality to the desktop version to play on the go. You will be able to play Babu88 live games, bet on cricket, participate in promotions, and make payments.
The Babu88 casino app has low system requirements and is optimized perfectly. This allows you to use it on any smartphone or tablet, whether it is a flagship gadget or an outdated device. The app is available for Android and iOS users. And if you can’t download the app for one reason or another, you can still play from your phone using the mobile browser version of Babu88.

Android
Downloading the Babu88 app on your Android smartphone is extremely easy. Familiarize yourself with these instructions before you start:
- Open any browser on the gadget.
- Navigate using the address bar to the official website of Babu88.
- Go to the left-side burger menu and find the option to download the app.
- Click on it and select the Android version.
- After successful download, open the installation APK file to run the installation.
- Launch the Babu88 app and play.

iOS
Downloading the Babu88 casino app on iOS is no more difficult than downloading it on Android. You will need to stick to roughly the same process. Below is a step-by-step instruction:
- Open Safari.
- Go to the Babu88 website.
- Once on the site, tap on the burger menu which is on the left side.
- Find a button to download the app at the bottom.
- Tap on it and select the iOS version.
- When the IPA file is downloaded, proceed to the Downloads folder and open it.
- Press OK to confirm the installation.
- Open the app to play on the go.

Babu88 Payments in Bangladesh
Babu88 is responsible for the subject of payments and provides only safe and fast payment tools. Besides, all of them are very familiar to Bangladeshi players as they use these payment systems in their daily lives as well.

| Payment Method | Limits, ৳ | Processing Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Nagad | Top-Up | 200-20,000 | Deposit Time | 0-4 hours |
| Withdrawal | 800-30,000 | Cashout Time | Up to 72 hours | ||
|
|
Rocket | Top-Up | 200-20,000 | Deposit Time | 0-4 hours |
| Withdrawal | Unavailable | Cashout Time | Unavailable | ||
|
|
bKash | Top-Up | 500-30,000 | Deposit Time | 0-6 hours |
| Withdrawal | 800-30,000 | Cashout Time | Up to 5 business days | ||
|
|
Upay | Top-Up | 500-30,000 | Deposit Time | 0-4 hours |
| Withdrawal | 800-30,000 | Cashout Time | Up to 72 hours | ||
License of Babu88 BD
Babu88 is a completely safe site, as it is licensed by the government of Curacao with document number 365/JAZ. This means that all the services that the site provides are legitimate in terms of legislation.
It should also be pointed out that the government of Bangladesh does not have any laws and regulations against offshore licensed online casinos, so playing on Babu88 is not a violation.

Support for Babu88 Bangladeshi Players
Babu88 online casino provides users with a reliable customer support service. They have access to various communication channels including chat, email, and social media. This ensures quick problem resolution, prompt response to queries, and overall user satisfaction. In case of questions or problems, the support team is available to provide friendly and professional assistance to users.

| Way to Contact | Description |
|---|---|
| Live Chat | Chat is located at the bottom right of the screen and is represented as a yellow circle with the Babu88 logo inside it |
| cs@babu88.com | |
| FAQ | Located in the footer, between the “About Us” and “Contact Us” tabs |
| Social media | The black and yellow social media logos can be found in the footer, on the left-hand side |
Babu88 Affiliate Program
If you want to cooperate with Babu88 casino, there is a great opportunity to do so, which is given by the affiliate program. With the help of it, you can attract players on the site and earn money. To become a partner of Babu88 you will only need to contact the manager, give them the necessary data, get access to the partner site, and start inviting new users. Your profit will depend on the number of users you invite and can reach 50%.
FAQ
Can I play free Babu88 games?
Yes, Babu88 provides a demo mode where the player can play without investment. This is a good way to practice and understand the rules of a particular game.
Can I contact the Babu88 Bangladesh support team by email?
Yes, in addition to live chat, you can use email if you want to ask a detailed question and attach screenshots.
Does the Babu88 website support Bangladeshi taka?
Of course, because Babu88 is focused on Bangladeshi players, you can use BDT on the site.
Will I get a welcome bonus for registering?
Yes, Babu88 in Bangladesh offers several welcome bonuses for new players. Depending on what you want to do on the site you can choose a bonus for slots, crash games, live casino, or betting.
Why do I need to verify my account?
Account verification is required for you to enjoy the full functionality of the Babu88 site. Without verification, you will not be able to withdraw funds, for example.
How many people can I bring in through the Babu88 affiliate program?
The number of users you can bring in using the affiliate program is unlimited, but at least one user is enough to start earning.
 Live Casino
Live Casino Slots
Slots Table Games
Table Games Fishing Games
Fishing Games Cricket Betting
Cricket Betting Live Bets
Live Bets iOS
iOS Android
Android Live chat
Live chat FAQ
FAQ Email
Email Social Networks
Social Networks